1-1. 프로그램 설명
<input>
사용자가 영어 단어를 입력한다. 입력 시 대 소문자 모두 입력 가능하다.
입력 된 단어에서 가장 많이 사용된 알파벳을 출력해줍니다.
<output>
가장 많이 사용된 알파벳이 여러 개일 경우 그 알파벳 모두를 출력해준다.
<핵심 개념>
c언어에서는 배열의 크기를 지정할 때 변수로 지정할 수 없다.
하지만 자바에서는 변수를 배열의 크기로 선언 할 수 있다. 그리고 자바의 2차원 배열에선 [2][] 이렇게 앞에 배열 크기만 선언 해주면 뒤의 배열 크기는 요소를 넣을 때 그 크기가 동적으로 정해진다.
1-2. 코드
package project1;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Mainclass {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
String inputstring;
char[] inputchar;
char[][] alphabet = new char[2][];
String alphabetstring_1 = "abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz";
String alphabetstring_2 = "ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ";
alphabet[0] = alphabetstring_1.toCharArray();
alphabet[1] = alphabetstring_2.toCharArray();
System.out.print("단어를 입력하세요[대소문자 모두 입력 가능]: ");
inputstring = sc.nextLine();
inputchar = inputstring.toCharArray();
int[] count = new int[26];
for(int i = 0; i < inputchar.length; i++) {
for(int j = 0; j < 26; j++) {
if(inputchar[i] == alphabet[0][j] || inputchar[i] ==alphabet[1][j] ) {
count[j]++;
}
}
}
int maxcount=0;
for(int i = 0; i <26; i++) {
if(count[i] > maxcount) {
maxcount = count[i];
}
}
System.out.print('\n'+"가장 많이 사용된 알파벳은:");
for(int i = 0; i <25; i++) {
if(count[i] == maxcount) {
System.out.print(" "+alphabet[0][i]);
}
}
}
}
1-3. 실행 결과



2-1. 프로그램 설명
컴퓨터가 1부터 100까지 임의로 숫자를 고르고 사용자가 이 숫자를 맞추는 게임이다.
총 상금은 천만원부터 시작하고 한 번 시도할 때마다 50만원씩 차감된다.
힌트는 총 2가지이며 첫 번째 힌트는 총 자리수를 알려주는 힌트이다.
두 번째 힌트는 젤 마지막 자리수를 알려주는 힌트이다.
힌트는 각각 한 번만 사용 가능하고 힌트 하나당 3000만원이 차감된다.
2-2. 프로그램 코드
package project1;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Mainclass {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println('\n'+"-----------------<숫자 맞추기 게임>--------------------------");
System.out.println("규칙1. 컴퓨터가 1~100까지 숫자 중 하나를 고르면 맞추면 최대 상금 천만원을 받습니다.");
System.out.println("규칙2. 힌트는 총 2번이고 힌트 사용시 300만원 차감됩니다.");
System.out.println("규칙3. 한번 시도 할 때마다 50만원씩 차감됩니다.");
System.out.println("시작 <1> , 종료<0>");
System.out.println("---------------------------------------------------------");
System.out.print(">");
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int on_off= -1;
while(true) {
on_off = sc.nextInt();
if(on_off == 1) {
for(int i = 0; i < 30; i++) {
System.out.println();
}
break;
}
else if(on_off == 0) {
System.out.println("게임을 종료합니다.");
return;
}
else {
System.out.print("다시 입력하세요>");
}
}
int computer_random = (int) (Math.random()*100 +1);
int total_money = 10000000;
int hint_1 = (int)(Math.log10(computer_random) +1); // 몇자리 수인지 알려주는 변수입니다.
int hint_2; // 마지막 자리수를 알여루는 변수입니다.
if(hint_1 ==1 ) {
hint_2 = computer_random;
}
else if(hint_1 ==2) {
hint_2 = computer_random % 10;
}
else {
hint_2 = 0;
}
int userinput;
int hint_user_input=-1;
int hint_1_on_off =0 , hint_2_on_off = 0;
while(true) {
outer_loop: //
while(true) {
System.out.print("전체 자리수 힌트 <1> , 제일 끝자리수 힌트 <2> , 힌트 사용 안함<3> 입력 >>");
while(true) {
hint_user_input = sc.nextInt();
sc.nextLine();
if(hint_user_input == 1 || hint_user_input == 2 || hint_user_input ==3) {
if(hint_user_input == 1) {
if(hint_1_on_off ==0) {
System.out.println("전체 자리수는 " + hint_1+ "자리입니다.");
total_money -= 3000000;
hint_1_on_off = 1;
break outer_loop;
}
if (hint_1_on_off == 1) {
System.out.print("힌트1 사용함 다시 입렵>>");
continue;
}
}
else if (hint_user_input == 2) {
if(hint_2_on_off ==0) {
System.out.println("제일 끝자리수는 " + hint_2+ "입니다.");
total_money -= 3000000;
hint_2_on_off = 1;
break outer_loop;
}
if (hint_2_on_off == 1) {
System.out.print("힌트2 사용함 다시 입렵>>");
continue;
}
}
else {
break outer_loop;
}
}
else {
System.out.print("다시 입력 >>");
}
}
}
//
System.out.println("현재 상금:" + total_money + "만원");
System.out.print("정답을 추측하여 보세요 입력>>");
userinput = sc.nextInt();
sc.nextLine(); // 엔터값 버퍼를 지워주는 부분입니다.
if(computer_random == userinput) {
System.out.println('\n');
System.out.println("축하합니다. 상금 : " + total_money +"만원 입니다!");
break;
}
else {
if(userinput - computer_random < 0) {
System.out.println("HIGH" + '\n');
}
else {
System.out.println("LOW"+ '\n');
}
total_money -= 500000;
}
if(total_money <= 0) {
System.out.println("끝났습니다. ");
break;
}
}
}
}
2-3. 프로그램 실행 결과
1) 제일 처음 프로그램 시작화면
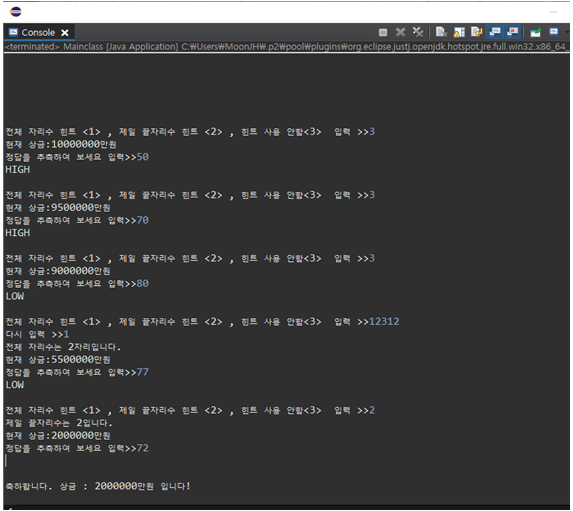
2) 게임 진행 실행화면입니다.
입력해야하는 값에 잘못 된 값을 입력하면 다시 입력받습니다.
3-1. 프로그램 설명
학점을 A+~F까지 과목별로 입력하게 되면 총 학점 점수의 평균을 출력해주는 프로그램이다.
제일 처음 사용자로부터 과목수를 입력받고 이후 과목명과 학점을 입력 받는다.
입력이 끝나면 학점이 높은 순으로 과목명과 학점을 출력해주고 학점의 평균점수를 출력해준다.
※ 자바에서는 문자열String클래스라는 개념이 존재하고 case문에 String문자열이 들어갈 수 있다.
3-2. 프로그램 코드
package project1;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Mainclass {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int total_subject_number;
System.out.print("총 과목수를 입력하세요>>");
total_subject_number = sc.nextInt();
sc.nextLine();
String[] subject = new String[total_subject_number];
String[] subject_score = new String[total_subject_number];
double[] subject_real_score= new double[total_subject_number];
for(int i = 0; i <total_subject_number; i++) {
System.out.print(i+1 +"번째 과목명을 입력하세요>>");
subject[i] = sc.nextLine();
System.out.print(i+1 + "번째 학점을 대문자로 입력하세요[A+~F]>>");
subject_score[i] = sc.nextLine();
}
for(int i =0; i<total_subject_number; i++) {
switch(subject_score[i]) {
case "A+" :
subject_real_score[i] = 4.5;
break;
case "A" :
subject_real_score[i] = 4.0;
break;
case "B+" :
subject_real_score[i] = 3.5;
break;
case "B" :
subject_real_score[i] = 3.0;
break;
case "C+" :
subject_real_score[i] = 2.5;
break;
case "C" :
subject_real_score[i] = 2.0;
break;
case "D+" :
subject_real_score[i] = 1.5;
break;
case "D" :
subject_real_score[i] = 1.0;
break;
case "F" :
subject_real_score[i] = 0;
break;
default:
break;
}
}
System.out.println('\n'+"-----------------------------------------------");
double k = 4.5;
for(int i =0; i<9; i++) {
for(int j=0;j<total_subject_number;j++) {
if(subject_real_score[j] == k) {
System.out.println(subject[j] +": " + subject_score[j]);
}
}
k = k-0.5;
}
double total_scor =0.0;
for(int i=0; i<total_subject_number; i++) {
total_scor +=subject_real_score[i];
}
total_scor = total_scor / total_subject_number;
System.out.println("총 학점 평균은 : " + String.format("%3f", total_scor) + "점입니다.");
}
}
3-3. 실행 결과
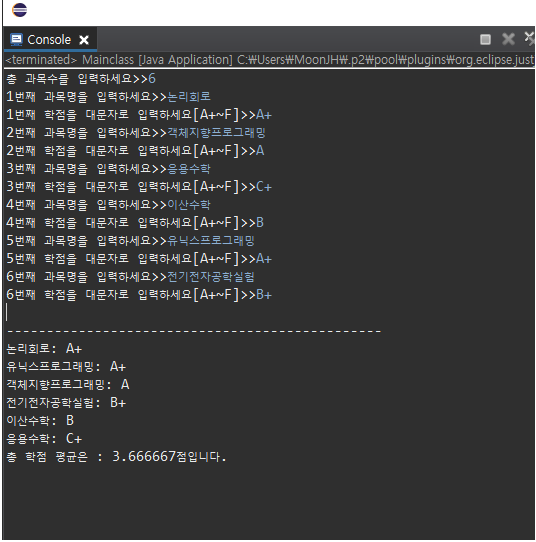
과목별 학점 입력이 모두 끝나면 최종 출력 결과는 학점이 높은 순서대로 출력해주고 총 학점 평균점수를 출력해준다.
4-1. 프로그램 설명
<input>
사용자로부터 두 원의 중심의 좌표와 반지름을 각각 입력받는다.
<output>
출력 결과는 두 원의 방정식을 출력해주고 두 원이 만나지 않는지 두 점에서 만나는지 접하는지 출력해주는 프로그램이다.
<핵심 개념>
이 프로그램에선 중심의 x, y 좌표, 반지름까지 한 번에 여러 정수를 입력받는다.
사용자가 입력 값을 입력하고 항상 Enter값을 누르게 된다. 이때 Enter값은 \r\n으로 두 문자에 해당하는 키이다.
Scanner클래스의 nextLine메소드를 제외하고 nextInt, next등 메소드는 사용자가 입력한 입력값을 읽을 때 마지막 끝에 Enter에 해당하는 \r\n을 버퍼에 그대로 남긴다.
이 상태에서 다시 Scanner 메소드를 호출하면 버퍼에 남아있는 \r\n을 두 문자를 읽어 사용자가 입력한 문자를 제대로 읽을 수 없게 된다.
따라서 항상 끝에 버퍼를 없애줘야한다.
nextLine메소드는 문자열을 읽는데 Enter 단위로 문자를 읽는다.
즉 문자열을 읽는데 \r\n까지 모두 읽는다.
그래서 nextInt메소드를 한번 호출 하고 nextLine메소드를 호출해서 버퍼에 남은 \r\n을 없애주고 다시 nextInt로 읽어야 정상적으로 사용자의 값을 읽을 수 있다.
4-2. 프로그램 코드
package project1;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Mainclass {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int a1, a2, r1, b1, b2 , r2;
System.out.print("첫 번째 원의 중심과 반지름을 각각 입력하세요[3 5 8]>>");
a1 = sc.nextInt();
a2 = sc.nextInt();
r1 = sc.nextInt();
sc.nextLine();
System.out.print("두 번째 원의 중심과 반지름을 각각 입력하세요[3 5 8]>>");
b1 = sc.nextInt();
b2 = sc.nextInt();
r2 = sc.nextInt();
double distance = Math.sqrt(Math.pow(a1-b1, 2) + Math.pow(a2-b2, 2));
double radius_sum = r1 + r2;
System.out.println("-----------------------------------");
if(distance > radius_sum) {
System.out.println("두 원은 만나지 않습니다.");
}
if(distance < radius_sum) {
System.out.println("두 원은 두 개의 교점을 가집니다.");
}
if(distance == radius_sum) {
System.out.println("두 원은 접합니다.");
}
System.out.println("첫 번째 원의 방정식: " + "(x-" + a1 +")" + " + (y-"+ a2+") = "+ r1*r1);
System.out.println("두 번째 원의 방정식: " + "(x-" + b1 +")" + " + (y-"+ b2+") = "+ r2*r2);
}
}
4-3. 실행 결과
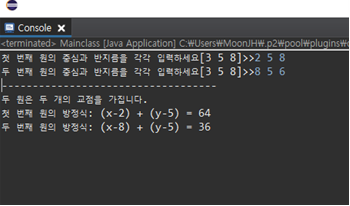
- 두 원이 서로 만나는 경우
- 두 원이 서로 만나지 않는 경우
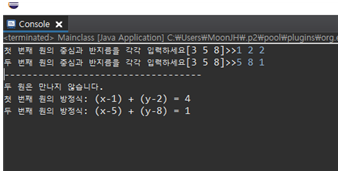
- 두 원이 동일한 경우
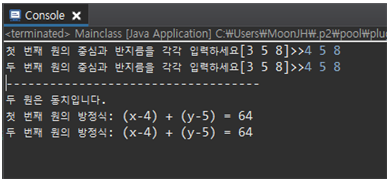
5-1. 프로그램 설명
구구단 2단부터 20단까지 출력할 수 있는 프로그램이다.
사용자로부터 몇 단부터 몇 단까지 출력할건지 구구단 두 범위를 입력 받는다.
입력 값이 2단보다 작거나 20단을 초과하면 다시 입력 받도록 do-while문으로 구성되어다.
5-2. 프로그램 코드
package project1;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Mainclass {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int start=0, end=0;
do {
System.out.print("출력하고 싶은 구구단 범위를 입력하세요[2단-30단]");
start = sc.nextInt();
end = sc.nextInt();
}
while(start < 2 || end > 30 || start ==end || start > end); {
System.out.println("<" + start + "-" + end + "단 구구단 출력!>");
for(int k = 0; k< 4; k++) {
System.out.println();
}
}
for(int p =1; p<=9;p++) {
System.out.print(" | ");
for(int i =start ; i<=(start+end)/2; i++) {
if(p*i>=10 && p*i<100) {
System.out.print(i+" x " + p + " = " + p*i+ " | ");
}
else if (p*i>=100) {
System.out.print(i+" x " + p + " = " + p*i+ " | ");
}
else
{
System.out.print(i+" x " + p + " = " + p*i+ " | ");
}
}
System.out.println();
}
System.out.println("");
for(int p =1; p<=9;p++) {
System.out.print(" | ");
for(int i = ((start+end)/2) +1 ; i<=end; i++) {
if(p*i>=10 && p*i<100) {
System.out.print(i+" x " + p + " = " + p*i+ " | ");
}
else if (p*i>=100) {
System.out.print(i+" x " + p + " = " + p*i+ " | ");
}
else
{
System.out.print(i+" x " + p + " = " + p*i+ " | ");
}
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}
5-3. 실행 결과
- 사용자로부터 5단부터 15단까지 입력을 받은 경우
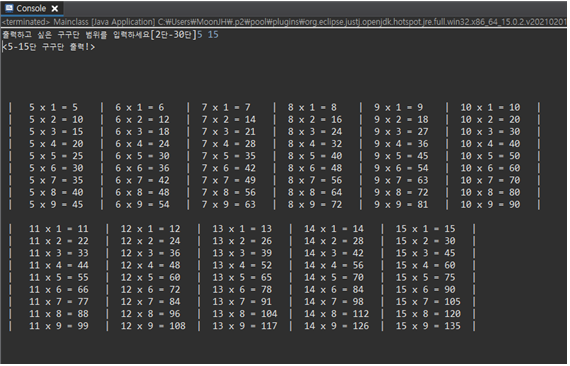
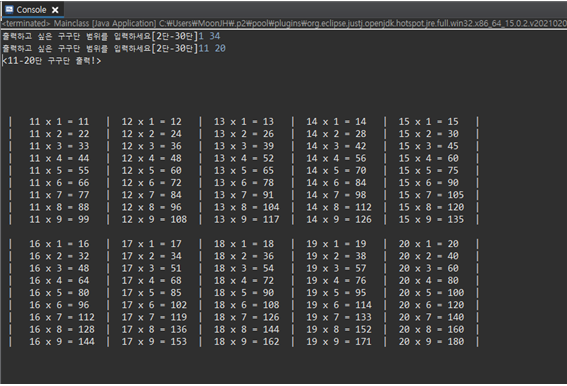
- 사용자로부터 11단부터 20단까지 입력을 받은 경우
최초 입력 시 잘못 된 입력을 할 경우 다시 입력 받는다.
'Java' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 5. 클래스 정리2 : final, 접근 제한자, (0) | 2022.01.20 |
|---|---|
| 4. 클래스 정리 1 : JVM 메모리 사용 영역, class 맴버 정리(Instance, static 맴버), overloading (0) | 2022.01.20 |
| 3. 1,2 차원 배열 선언 문법 (0) | 2022.01.17 |
| 2. 자바 명령어 도구(javac, java) (0) | 2022.01.17 |
| 1. JVM, JDK, JRE (0) | 2022.01.17 |